With the onset of cold weather, residential and commercial property owners strive to reduce heat loss in their buildings. To avoid overpaying for heating, they need suitable radiators that offer increased heating efficiency, reliability, and easy installation. The Russian market offers classic cast iron, steel, modern light-alloy, and bimetallic options. The latter category is in high demand due to its high heat transfer coefficient, attractive technical characteristics, and reasonable cost.
Buyers are faced with the challenge of correctly calculating the number of sections and the total fuel capacity, taking into account the area to be heated. Preliminary calculations will help reduce the cost of purchasing and installing radiators to create a comfortable microclimate in the rooms of a home, city apartment, or office. How to determine the number of sections for bimetallic heating radiators?
Advantages of bimetallic heating radiators
The core and vertical heat-conducting channels of the ribbed bimetal are made of steel, and the outer layer of the radiator is cast from aluminum alloy. These prefabricated sections of Stout bimetallic heating radiators can withstand pressures exceeding 20 atmospheres at coolant temperatures up to 1300°C. The technical datasheet for each sectional model contains detailed technical specifications. Bimetallic heating units can withstand extreme loads when installed in high-rise buildings and country cottages with autonomous heating. Professional preliminary calculations of power, coolant volume, and the number of sections for economical space heating reduce one-time and monthly heating costs.
Installation advantages:
- Reliability. The warranty period is 20 years under intensive use.
- Increased power. The original technical parameters of the radiators exceed those of aluminum form factors.
- Aesthetics. The compactness and appearance of monolithic sections complement classic or creative interiors.

The listed features of bimetallic radiators increase the competitiveness of heating units for work areas in living rooms and utility rooms. The disadvantage of bimetallic radiators is the price of prefabricated sections, which is higher than that of similar radiators made from simpler and cheaper materials. Traditional radiators are inferior in heat output, so using the original calculation formula reduces the number of bimetallic prefabricated sections, reducing the project cost.
How to correctly calculate the heat output of equipment
The calculation method is based on current building codes. Heating 1 m² of an office, warehouse, or apartment room requires 100 W of heat. The datasheet for bimetallic heating radiators from Rommer or another preferred brand specifies the heat output of each segment. Dividing the calculated power by the value of a single section yields the number of fins in a monolithic or prefabricated radiator.
A rapid calculation of the power of each section requires no specialized skills or time-consuming formula calculations. A single segment of a bimetallic radiator increases heat output by 10% compared to traditional cast iron radiators. The small power reserve is compensated by the buildup that will eventually form on the radiator’s inner walls. The room temperature can be controlled using the coolant flow control valves.
Rules for calculating the number of sections
User reviews of the chosen manufacturer will help you choose the right heating unit size. Recommendations and photos for proper installation, published online, will help prevent common mistakes. DIY installation will be successful if carried out correctly. To avoid errors in calculating the heat capacity and securely attaching the unit to the wall, we recommend seeking the help of experienced professionals.
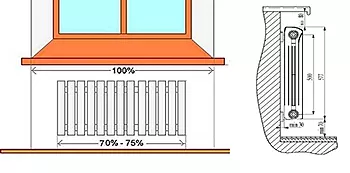
When determining the heating capacity, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The material and thickness of the room’s walls;
- The dimensions, type, and number of windows in the room;
- The presence of additional heating;
- The height of the ceilings or interfloor slabs;
- Temperature and humidity levels;
- the presence of load-bearing walls and non-load-bearing partitions.
Experts recommend maintaining a distance of 20-50 millimeters from the wall during installation, ignoring the thickness of the reflective insulation. The bottom edge of the radiator should be positioned 10 centimeters above the floor to increase heat transfer.
How to calculate the power per 1 m² of a room yourself
To calculate the heating power consumption, consider the radiator size and manufacturer’s recommendations. An average figure of 100 watts per square meter applies if the room has one load-bearing wall with a window and three partitions. The height of the interfloor opening should not exceed 2.7 meters for the calculation results to be valid. As the number of load-bearing structures in the room increases, an additional 20-30% is added to the calculated power for each external wall and additional window. Window openings increase heat loss, so the total heating power of the usable area must be calculated.
Other reasons for using increasing coefficients:
- windows facing north – +10%;
- the device is installed in a window recess – +5%;
- the outer side of the radiator is covered with a decorative panel – +15%.

Thermal efficiency indicators are summed to obtain a reliable result, expressed numerically. All that remains is to multiply the bimetallic radiator calculation results by the area of the room being equipped, which is calculated by multiplying the length by the width, in meters. The dimensions of each section are selected taking into account the free installation space between the windowsill and the floor. It is recommended to add one or two fins to compensate for heat loss and ensure a comfortable temperature.
How to calculate the number of sections
For complete and optimal heating of the usable volume of living spaces in a country house, apartment, or office space, an accurate calculation is required. To simplify the task, let’s consider the calculation principle using a 30 m² home as an example. If the ceiling height does not exceed 2.7 meters, and the power of each radiator segment is 200 W, the formula would be: 30 x 100/200 = 15. A small one-room apartment would require approximately 15 fins, located in the kitchen and in the room under the window.
This is how the calculation of bimetallic radiator sections for uniform heating of rooms with one external wall looks in practice. If there are two external capital structures and a pair of windows, a 30% adjustment coefficient is applied, by which the resulting figure is multiplied. For standard heating, three radiators with 6 sections each would need to be purchased, for a total of 18 fins filled with coolant.


